线程生命周期
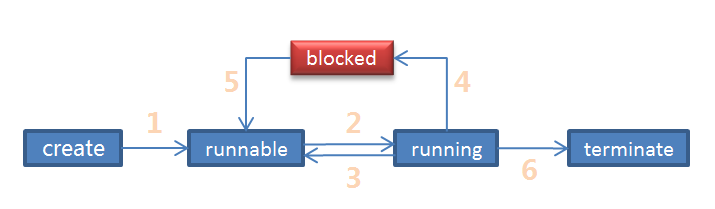
- 调用start()方法
- 获得CPU使用权
- 失去CPU使用去或调用yield()方法
-
- run()方法执行完毕
- 调用线程的stop()方法
- 执行中抛出Exception且未进行处理
创建线程
- 继承 Thread 类
- 实现 Runnable 接口
- Callable
- thread pool
public class Bounce
{
static class Basketball extends Thread
{
@Override
public void run()
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
static class Football implements Runnable
{
@Override
public void run()
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Basketball b = new Basketball();
b.start();
Football f = new Football();
new Thread(f).start();
// callable
new Thread(new FutureTask<Object>(new Callable<Object>() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception
{
for (byte i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i * 2);
}
}
return null;
}
})).start();
// thread pool
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
service.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run()
{
for (byte i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i * 3);
}
}
}
});
service.submit(new Callable<Object>() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception
{
for (byte i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i * 7);
}
}
return null;
}
});
}
}常用方法
- join
- interrupt 1
- setDaemon(Boolean on)
- 作用:将此线程设置为守护线程或用户线程(on为true)。当仅有守护线程运行时,JVM将退出。
- 应用场景例:client和server之间建立长连接,将心跳检测线程(辅助)设置为daemon thread,当其余线程(如负责收发数据线程)结束后,仅剩daemon thread会使JVM退出,程序随之终止,无需手动停止辅助线程运行。
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Thread t1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run()
{
while (true) {
if (isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println(getName() + " is interruped.");
break;
}
}
}
};
t1.start();
Thread main = Thread.currentThread();
Thread t2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run()
{
t1.interrupt();
main.interrupt();
}
};
t2.start();
try {
t1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is interrupted");
}
}线程同步
- 线程同步方式
- synchronized同步代码块
- synchronized同步方法
- 以this为锁
- 以ClassName.class为锁
-
线程同步问题
- 死锁:进程Thread-0拥有锁-x,想使用锁-y;同时,进程Thread-1拥有锁-y,想使用锁-x
class DeadLock
{
private final Object LOCK1 = new Object();
private final Object LOCK2 = new Object();
public void method1()
{
synchronized (LOCK1) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (LOCK2) {
}
}
}
public void method2()
{
synchronized (LOCK2) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (LOCK1) {
}
}
}
}
public class DeadLockTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DeadLock deadLock = new DeadLock();
new Thread() {
public void run()
{
deadLock.method1();
}
}.start();
new Thread() {
public void run()
{
deadLock.method2();
}
}.start();
}
}
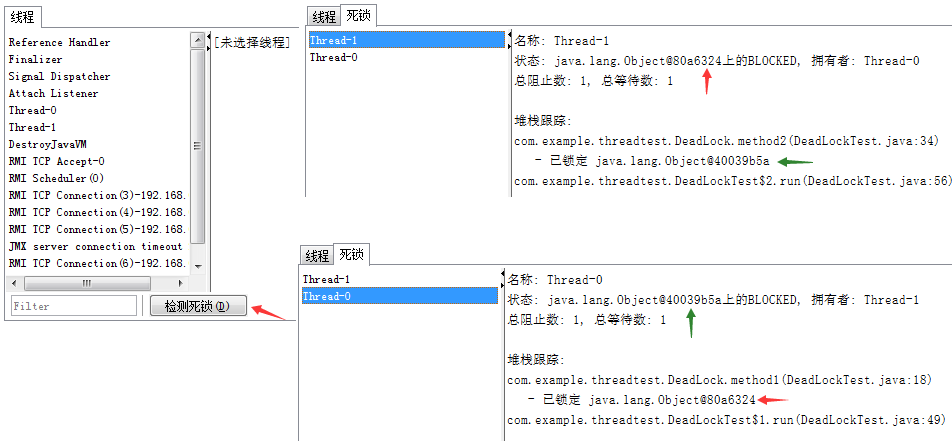
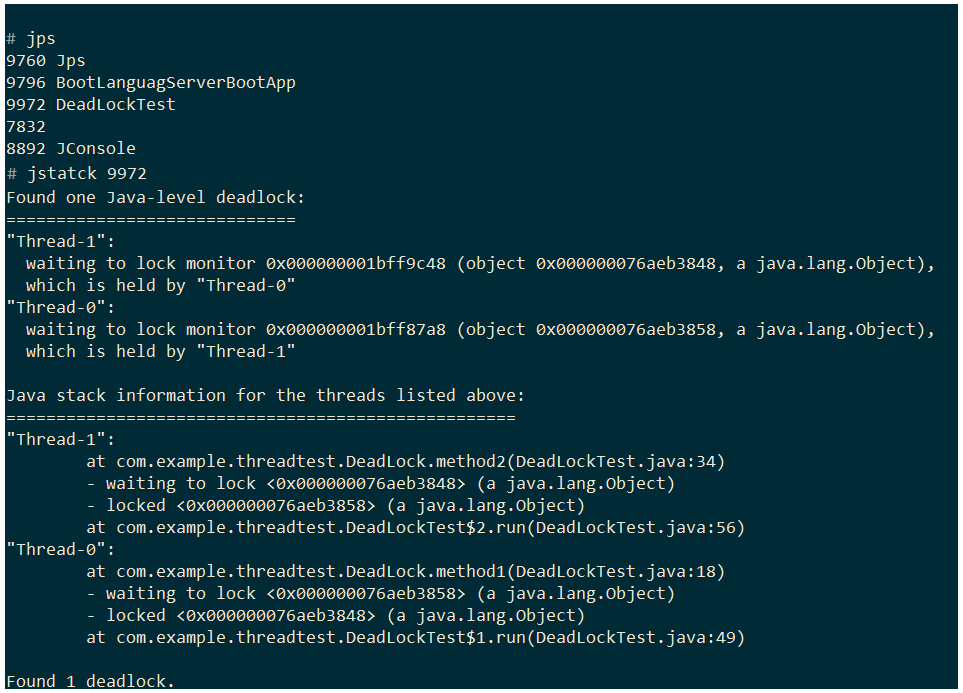
线程通信
捕获线程异常
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 10, b = 0;
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1_000);
int result = a / b;
System.out.println(result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler((t, e) -> {
System.out.println(t);
System.out.println(e);
Arrays.asList(Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace())
.stream()
.filter(m -> !m.isNativeMethod())
.forEach(m -> Optional.of(m.getClassName() + "." + m.getMethodName() + ":" + m.getLineNumber()).ifPresent(System.out::println));
});
thread.start();
}ThreadGroup
辅助工具
- jconsole:Java监视和管理控制台
- jps:运查看行中的Java进程id及进程名称
- jstack:连接至运行中/挂起的进程等
- javap -c:反汇编class文件